
- 23rd January 2026
Table of Contents
- FROM ANCIENT ROYALTY TO MODERN SUPERFOOD
- THE FORBIDDEN HISTORY AND ORIGIN OF CHAKHAO
- THE SCIENCE OF PURPLE: WHY BLACK RICE IS NUTRITIONALLY SUPERIOR
- COMPARISON BETWEEN NUTRIENT CONTENTS OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF RICE
- KEY HEALTH BENEFITS: DIABETES, HEART HEALTH, AND BEYOND
- COOKING THE PERFECT GRAIN: METHODS AND TIPS
- WHO SHOULD BE CAREFUL?
- TAKE-HOME POINTS
FROM ANCIENT ROYALTY TO MODERN SUPERFOOD
For centuries, the choice in the kitchen was limited to white or brown rice, but a third super option is taking center stage. Black rice, once a hidden treasure of the Northeast, has captured the national spotlight for its remarkable healing properties. At the Dr. Pankaj Kumar Medical and Lifestyle Clinic, we focus on evidence-based nutrition to help our patients achieve lasting wellness. Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently brought this grain into the mainstream, hailing it as a superfood in states like Manipur, Assam, and Meghalaya. His endorsement highlights its deep medicinal value and its role in transforming the lives of local farmers. To understand the excitement, we must look back at the grain's unique forbidden history.
THE FORBIDDEN HISTORY AND ORIGIN OF CHAKHAO
The cultural roots of black rice are as deep as its dark pigment. In the Indian state of Manipur, the grain is known as Chakhao. In the local language, Chak means rice and Hao means delicious. Traditionally, it has been a staple of ceremonial feasts, with specific landraces like Chakhao poireiton being prized for superior productivity and delicacy.
This sense of exclusivity mirrors its history in ancient China, where it was famously called forbidden rice or emperor's rice. Because of its high nutritional density and rarity, it was reserved solely for royalty and forbidden to common people. When raw, the grain is a deep, obsidian black. Upon cooking, it undergoes a striking transformation into a rich purple. It is celebrated for its signature nutty flavor and chewy texture, making it a distinct alternative to refined varieties.
THE SCIENCE OF PURPLE: WHY BLACK RICE IS NUTRITIONALLY SUPERIOR
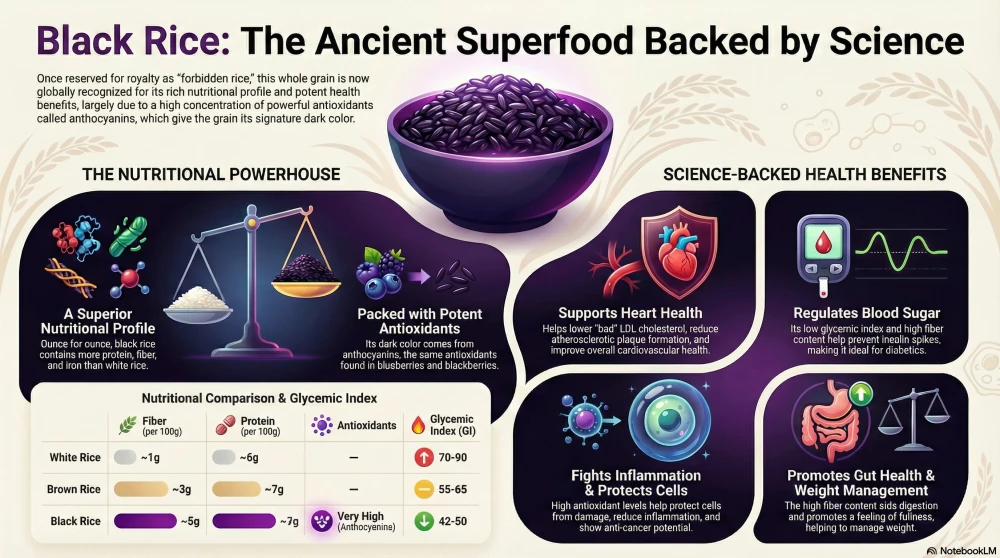
The dark pigment of black rice is a marker of its nutritional power. The primary compounds responsible for this color are anthocyanins, powerful antioxidants also found in blueberries. Expert research from Dr. Zhimin Xu highlights that a spoonful of black rice bran contains more health-promoting anthocyanin antioxidants than a spoonful of blueberries, while providing more Vitamin E, more fiber, and less sugar.
Beyond antioxidants, black rice is a complete plant-based protein source containing 18 different amino acids. It is also dense with essential minerals including iron, zinc, copper, carotene, magnesium, and phosphorus. When compared to white rice, the clinical advantage is clear:
COMPARISON BETWEEN NUTRIENT CONTENTS OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF RICE
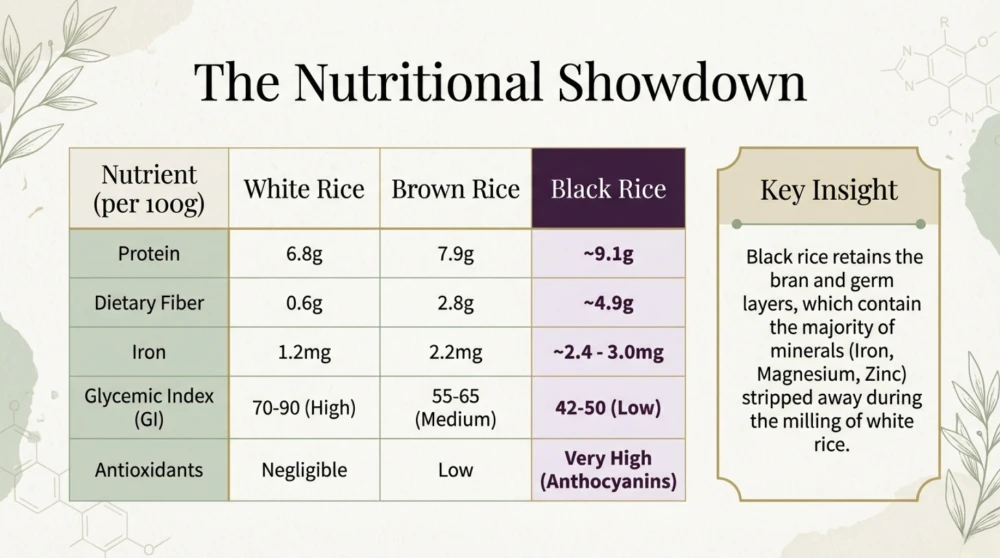
This nutritional foundation provides the mechanism for several medicinal benefits, particularly regarding common lifestyle diseases.
KEY HEALTH BENEFITS: DIABETES, HEART HEALTH, AND BEYOND
Clinical reviews and nutritional studies have identified several key areas where black rice acts as a medicinal grain:
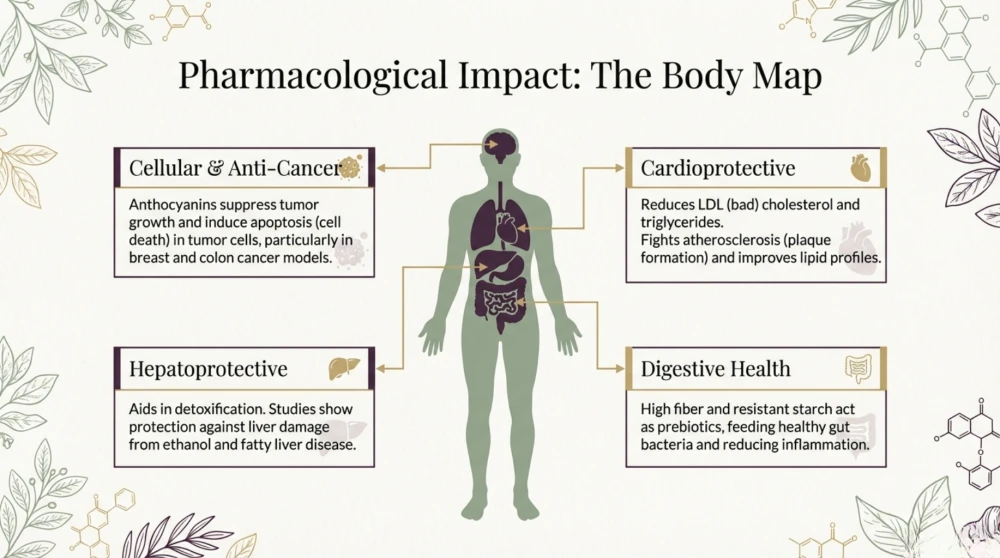
- Diabetes and Blood Sugar Regulation: Black rice is a low-glycemic index (GI) grain. Because it is rich in fiber and resistant starch, it slows the release of glucose into the bloodstream. Research shows that black rice anthocyanins can improve insulin sensitivity, making it a safer choice for those managing diabetes.
- Heart Health: This grain provides powerful cardiovascular protection. A clinical study in women demonstrated that consuming black rice daily reduced the risk of heart disease and stroke by 57 percent. The antioxidants help improve HDL (good cholesterol) while reducing harmful LDL particles and triglycerides.
- Detoxification and Liver Health: Black rice possesses hepatoprotective qualities. It supports liver function and aids in the elimination of toxins from the body by reducing oxidative stress and protecting liver cells from damage.
- Eye Health: The grain is high in antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin, which are essential for protecting the eyes from oxidative damage and reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
- Weight Management: Black rice helps regulate appetite through the secretion of leptin, a hormone that signals fullness to the brain. Its high fiber and protein content promote satiety, helping individuals manage weight effectively.
COOKING THE PERFECT GRAIN: METHODS AND TIPS
To maximize the nutritional benefits and achieve the best texture, black rice requires specific preparation.
- The Soak and Simmer Method: This is the preferred clinic-style advice for optimal digestion. Soaking the rice overnight is essential to soften the hard outer bran layer and improve nutrient absorption.
- The Pot Method: Use a ratio of 1 cup of soaked rice to 2.5 cups of hot water. Bring to a boil, then simmer on low heat for 30 to 40 minutes. Keep the grains firm rather than mushy to maintain the best nutritional profile.
- The Pressure Cooker Method: For a quicker option, soak the rice for at least 30 minutes. Use a 1:2 ratio of rice to water and cook for 2 to 3 whistles on medium flame.
- The Expert Tip: Use the cool and reheat trick. Allowing cooked rice to cool before reheating it boosts the levels of resistant starch, which further reduces the glucose rise after eating.
WHO SHOULD BE CAREFUL?
While black rice is an exceptional health food, it should be introduced with professional balance:
- Digestive Adjustment: Because black rice is significantly higher in fiber than white rice, it can cause gas or bloating if added to the diet too quickly. Introduce it gradually.
- Phytic Acid and Arsenic: Like many whole grains, black rice contains phytic acid, which can affect mineral absorption if consumed in excess. Additionally, whole grain varieties can have higher arsenic content than polished rice, making moderation important.
- Medical Consultation: Individuals on specific medications or those who are pregnant should always consult their doctor before making major dietary changes, as the grain's potent properties can interact with metabolic processes.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- Black rice is a superfood with 18 amino acids and deep cultural roots as Chakhao in Manipur.
- It offers higher antioxidant strength than blueberries, specifically in anthocyanins and Vitamin E.
- Daily consumption has been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke by 57 percent in clinical studies.
- It is a superior choice for diabetes management due to its low Glycemic Index and high fiber content.
- Always soak the grain overnight and consider the cool and reheat method to maximize resistant starch.
This guide was brought to you by the expert team at Dr. Pankaj Kumar Medical and Lifestyle Clinic, helping you achieve better health through evidence-based nutrition.














