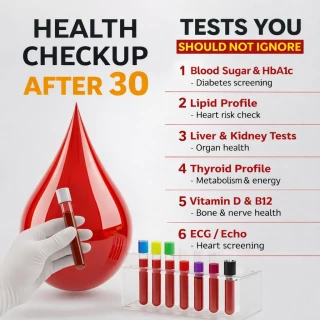
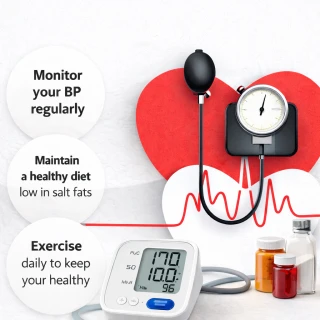
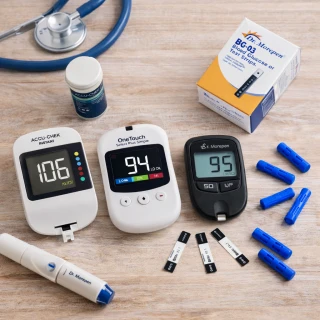
- 14th March 2024
Table of Contents
I. Introduction
This article emphasizes the importance of diet and nutrition in maintaining optimal health and well-being. It provides clear explanations, practical tips, and evidence-based recommendations to help readers make informed choices about their dietary habits. It aims to promote longevity, enhance immune function, support mental health, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
II. Fundamentals of Nutrition
Macronutrients
Macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, are essential for maintaining a balanced diet and achieving optimal health. Carbohydrates, found in grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, provide energy and support brain function. Proteins, composed of amino acids, are crucial for tissue building, immune function, and metabolism regulation. Fats, found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, are essential for energy storage, hormone production, and nutrient absorption. Understanding these macronutrients is crucial for making informed choices about dietary habits and achieving optimal health.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are essential vitamins and minerals required by the body in small amounts for various physiological functions, such as metabolism, immune function, and cell growth. They play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Vitamins are water-soluble and fat-soluble, and are classified into macrominerals and trace minerals. Minerals are inorganic elements found in foods and play a vital role in bone formation, muscle contraction, and nerve transmission. Water is essential for regulating body temperature, transporting nutrients, removing waste products, and lubricating joints. Understanding micronutrients, deficiencies, and sources is crucial for optimizing nutritional intake and supporting overall health.
III. Dietary Guidelines
RDAs are guidelines set by health authorities to guide individuals on the recommended intake of essential nutrients for optimal health. They consider factors like age, sex, and life stage. The Food Pyramid or Plate is a visual representation that illustrates the recommended proportions of food groups for a balanced diet. Understanding these tools helps individuals make healthier choices and achieve a balanced diet. Serving sizes are standardized portions of food recommended for consumption, guiding calorie intake and ensuring appropriate nutrients are consumed without overeating.
IV. The Role of Diet in Health
This section discusses the importance of preventing chronic diseases, maintaining a healthy weight, boosting immunity, and enhancing mental health. It highlights the role of diet, exercise, stress management, and lifestyle factors in reducing the risk of chronic diseases. It also discusses strategies for maintaining a healthy weight, such as setting realistic goals, making sustainable lifestyle changes, and seeking support when needed. It also discusses the role of nutrition, sleep, exercise, and stress management in boosting immunity. It concludes by highlighting the connection between nutrition and mental health, emphasizing the need for a balanced diet, stress-reducing activities, and adequate sleep to improve overall health and quality of life.
V. Understanding Food Labels

The Nutritional Facts Panel is a label on food products that provides information on nutrient content and serving size. It helps consumers make informed dietary choices and manage nutrient intake based on individual health goals. The Ingredients List is a detailed inventory of food components, helping consumers identify allergens, additives, and preservatives. Health claims on food packaging suggest a relationship between nutrient or ingredient and health outcomes. Understanding these claims is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions about the nutritional value and potential health benefits of food products.
VI. Different Dietary Approaches
The Mediterranean Diet is a dietary pattern based on traditional Mediterranean diets, focusing on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fish. It is associated with health benefits like reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, and certain chronic conditions. Vegetarian and vegan diets emphasize plant-based foods while excluding animal products. Low-carb and keto diets restrict carbohydrate intake while focusing on higher fat consumption and moderate protein intake. These diets are associated with weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and enhanced satiety. Intermittent fasting cycles between periods of eating and fasting, focusing on when to eat. It has been linked to weight loss, improved metabolic health, and enhanced cellular repair processes.
VII. Building a Healthy Plate
Whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, lean proteins, and healthy fats, are nutrient-dense and naturally processed. They provide essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, supporting overall health. Portion control helps maintain a healthy balance of nutrients and calorie intake, preventing overeating and maintaining a healthy weight. Meal planning and prepping streamline the cooking process, allowing individuals to make healthier choices throughout the week. These practices can save time, reduce stress, and support healthier eating habits and overall well-being.
VIII. Addressing Common Nutrition Myths
This section delves into two key aspects of nutrition: debunking misconceptions and clarifying confusions. It discusses common misconceptions about nutrition and health, such as myths about certain foods or dietary patterns. It also delves into the challenges of navigating nutrition information and promoting healthier eating habits. The goal is to provide clear, evidence-based explanations to help individuals make informed decisions about their health.
IX. Understanding Special Dietary Needs
Nutrition is crucial during pregnancy, lactation, childhood, aging, and sports. Pregnant and lactating women need to consume essential nutrients like folic acid, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids to support fetal growth and milk production. Childhood nutrition is essential for infants, toddlers, children, and adolescents, providing essential nutrients for physical and cognitive development. As individuals age, their nutritional needs may change, leading to changes in appetite, metabolism, and chronic disease risk. Older adults need adequate protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals to support healthy aging and prevent age-related conditions. Sports nutrition focuses on optimizing diets and nutritional intake for athletes to support performance, training adaptations, and recovery. By prioritizing sports nutrition, athletes can optimize training outcomes, reduce injury risk, and achieve athletic goals.
X. Seeking Professional Guidance
Registered Dietitians (RDs) are nutrition and dietetics experts. They have extensive experience translating scientific research into healthy diet advice. A bachelor's degree in nutrition or a related field, an accredited internship, and a national exam are required for RDs. This section discusses how Registered Dietitians provide evidence-based nutrition counseling, personalized meal planning, and support for chronic disease management, weight loss, sports nutrition, and more. Registered Dietitians can help people reach their nutrition goals and improve their health and quality of life.